AI Agent Washing
Gartner estimates only about 130 of the thousands of agentic AI vendors are real.
I remember while working for a large enterprise, when they switched over from a Waterfall approach to projects and adopted Agile.
Virtually overnight Project Managers (PMs) changed into Scrum Masters.
The term retread was even used…we are retreading our PMs to become Scrum Masters.
Often I think the same is happening now with the introduction of AI Agents.
Existing AI Assistants, RPA and chatbots without any agentic capacities or agency are be retreaded as AI Agents.
AI Agent Hype Is Colliding With Reality
Thanks for reading Cobus Greyling on LLMs, NLU, NLP, chatbots & voicebots! Subscribe for free to receive new posts and support my work.
Legacy systems with no level of Agency or ability to decompose compound complex tasks into sequential sub-tasks.
Gartner estimates only about 130 of the thousands of agentic AI vendors are real.
Over 40% of agentic AI projects will be canceled by the end of 2027, due to escalating costs, unclear business value or inadequate risk controls, according to Gartner, Inc.
ROI
Many use cases positioned as agentic today don’t require agentic implementations.
AI Agents That Matter
Thanks for reading Cobus Greyling on LLMs, NLU, NLP, chatbots & voicebots! Subscribe for free to receive new posts and support my work.
From a business perspective, there needs to be a strong business use-case when implementing AI Agents, and this should revolve around proven cost savings or increase in revenue.
Hence the operational cost of AI Agents are important.
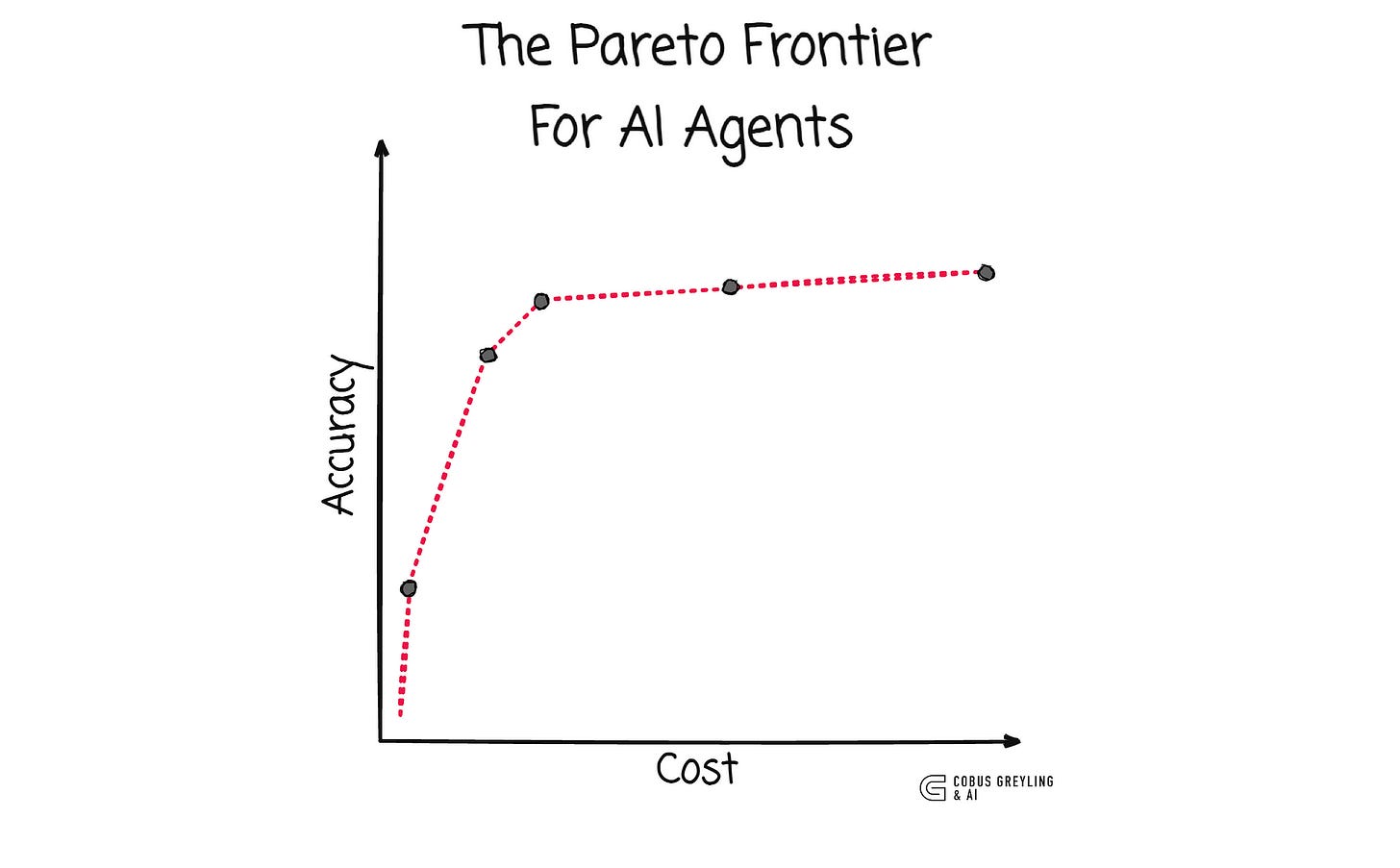
Visualising the cost and accuracy of AI Agents as a Pareto frontier reveals opportunities to design agents that optimise both, leading to lower costs without sacrificing performance. This approach can also extend to other factors like latency.
The total cost of running an AI Agent consists of fixed and variable costs.
Fixed costs arise from one-time efforts like tuning parameters (e.g., temperature or prompt design) for a task, while variable costs depend on usage and scale with the number of input and output tokens.
Over time, variable costs tend to dominate as agents are used more frequently.
By focusing on joint optimisation, it is possible to balance fixed and variable costs. Investing upfront in refining agent design can lower ongoing operational costs, such as by creating shorter prompts or more efficient few-shot examples that maintain accuracy.
Most agentic AI projects right now are early stage experiments or proof of concepts that are mostly driven by hype and are often misapplied. Gartner
AI Agent Definition
Unlike traditional automation, an AI Agent can break down problems into sequential steps/sub-tasks, handling each individually.
Through iterative cycles of thought, action, and observation, the AI Agent adapts its responses based on feedback.
AI Agents also utilise a range of tools for interacting with systems like APIs or web searches, with their effectiveness shaped by the variety of these tools, enabling them to handle diverse tasks and execute intricate workflows.
Each tool has a description in natural language, the AI Agent then matches the sub-task at hand with the tool description to know which tool to match with which sub-task.
Tools can include functionality like Web Search APIs, Data Retrieval APIs, Code Execution Environments, Browser Automation Tools, Natural Language Processing (NLP) APIs, File Management Systems, ACI-Tools, vision, etc.
Chief Evangelist @ Kore.ai | I’m passionate about exploring the intersection of AI and language. From Language Models, AI Agents to Agentic Applications, Development Frameworks & Data-Centric Productivity Tools, I share insights and ideas on how these technologies are shaping the future.