Large Language Models, Foundation Models & Multi-Modal Models
How did we go from LLMs, to Foundation Models and now Multi-Modal Models, with GPT-4 being described as a Multi-Modal Model?
Let’s first address the parameter size of GPT-4, there is incredible hype around the subject; I have addressed it in detail in a prior article. You will see there is a clear progression of parameter size which serves as a good indicator in terms of sheer parameter size.
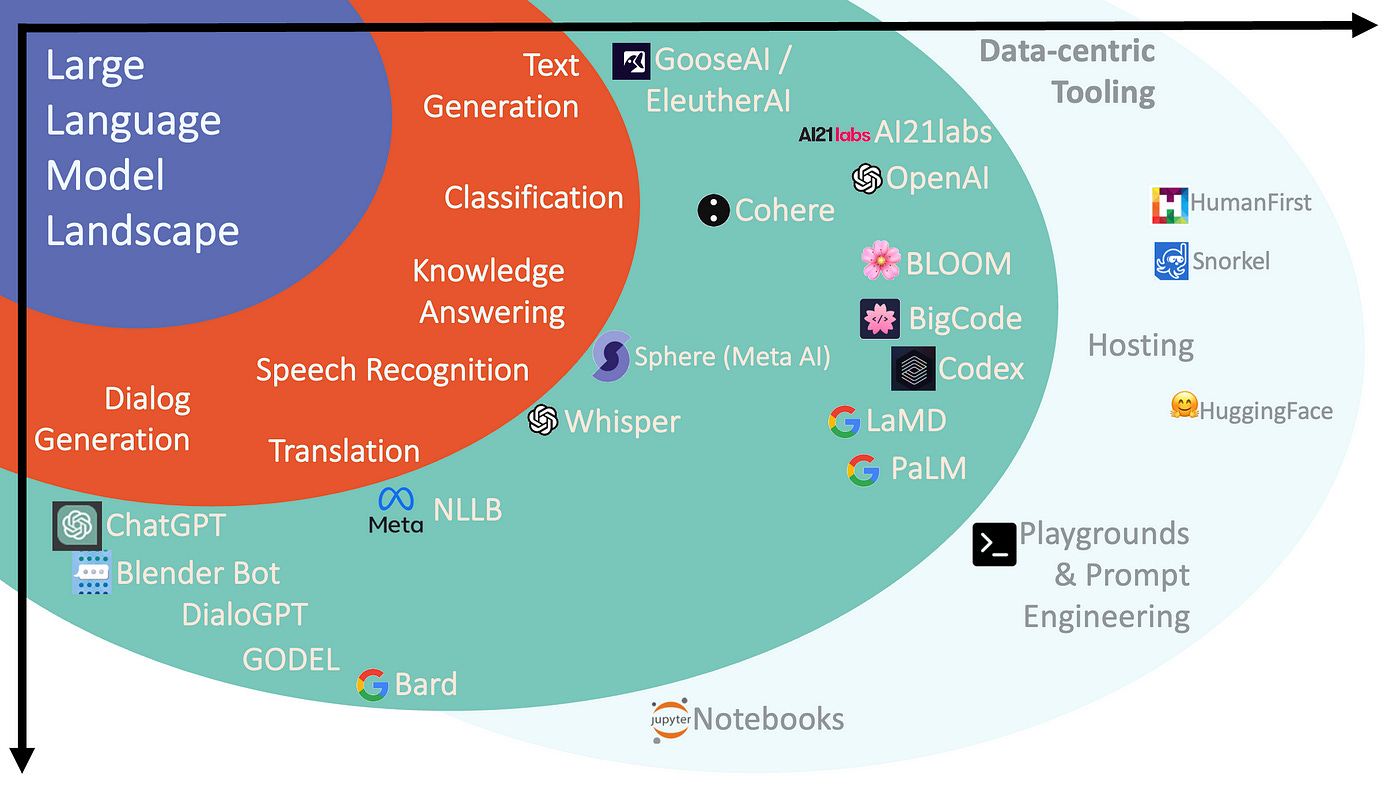
Secondly, Large Language Models (LLMs) have seen steady expansion in functionality.
As the chart below indicates, LLMs have grown in functionality from text generation, into areas like classification, knowledge answering, translation, ASR, etc.
A case in point, is a LLM like Bard focussing on search, as described by Google.
And of late, there has been much focus on Dialog Generation or chain of thought reasoning, especially with ChatGPT.
But in fact dialog generation has been around for a while with other models addressing the challenge of dialog-state-creation and conversation context management.
The models related to dialog generation is listed below ChatGPT in this image. ⬇️
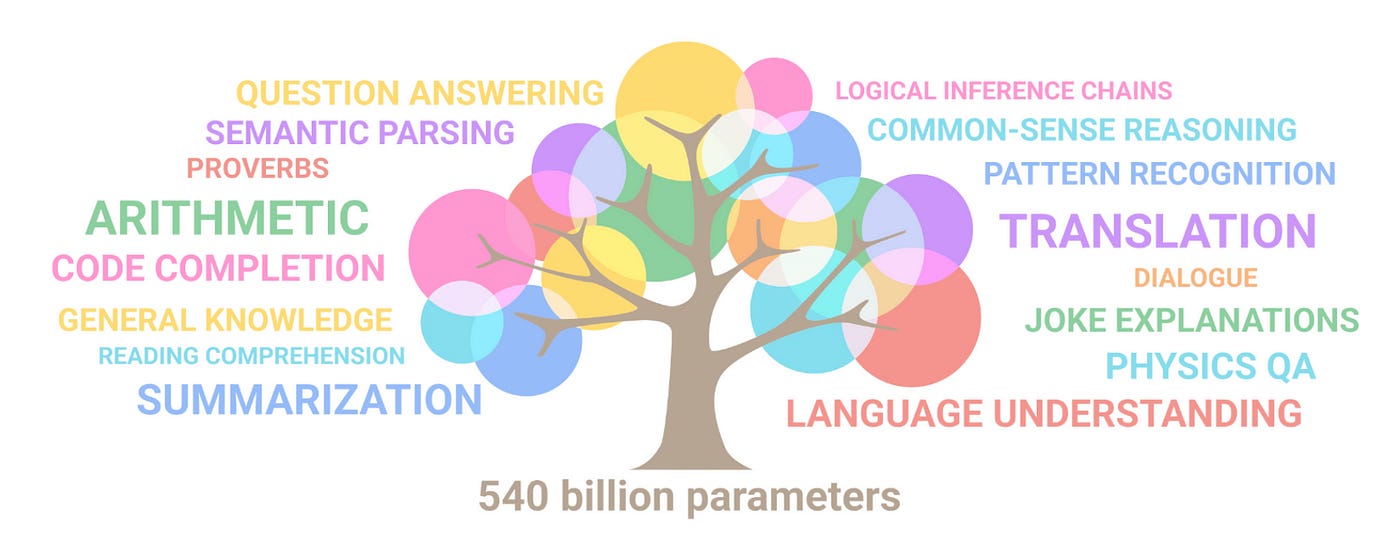
Consider the image below, as used by Google to describe the functionality of the PaLM foundation model. Still very much language related, whilst branching out into various specific areas.
Some thought it apt to rather describe LLMs as Foundation Models, moving away from a language only ambit.
The reasoning for this is that Large Models will sprawl into other none-language related tasks, but still remain the foundation of many applications and services.
A Foundation Model can be language only related in terms of functionality, or it can also cover other modalities like voice, images, video, etc.
Below, in the words of Sundar Pichai:
Now, our newest AI technologies — like LaMDA, PaLM, Imagen and MusicLM — are building on this, creating entirely new ways to engage with information, from language and images to video and audio. We’re working to bring these latest AI advancements into our products, starting with Search.
All of this begs the question, will a multi-modal model then be a large model which combines different modalities into one?
Is this what GPT-4 will encompass? A combination of OpenAI models like gpt-3.5-turbo, Whisper Version 2, DALL-E2 and Jukebox?
We will introduce GPT-4 next week, there we will have multi-modal models that will offer completely different possibilities — for example, videos…
~ Andreas Braun (Microsoft Germany CTO)
What I find interesting of Visual ChatGPT is that it is still very much conversation and dialog based, as seen in the demo below from Microsoft.
This indicates that the human-computer interface will still be very much conversation based. With the human describing their request in natural language and the Foundation Model leveraging its multi-modal capability to yield a result.
Obviously Foundation Models will have the modal capability to execute the request. Hence there will be a discovery element from users to understand which modalities form part of the model.
As the use of LLMs increases, there will be a growing need for fine-tuned models. And by implication a need to convert unstructured data into structured NLU & NLG design data.
Building custom and accurate NLU datasets from unstructured data, with focus on voice and text data will become increasingly important.
This will allow for solving for the long-tail of intent distribution and assist in identifying the correct taxonomy for labelling.
NLU design is a data-centric solution to this problem, which follows a human-in-the-loop, bottom-up approach to accelerate custom Conversational AI and CCAI implementations.
⭐️ Please follow me on LinkedIn for updates on Conversational AI ⭐️
I’m currently the Chief Evangelist @ HumanFirst. I explore and write about all things at the intersection of AI and language; ranging from LLMs, Chatbots, Voicebots, Development Frameworks, Data-Centric latent spaces and more.