Measuring Agents in Production
What are the technical strategies that make AI Agent deployments successful?
Key Trends in Developer Adoption of Autonomous AI Systems
Developers are increasingly favouring tightly bounded autonomy over fully autonomous systems, prioritising controlled environments where AI can operate reliably without risking unchecked errors or ethical lapses.
Evaluations Remain Informal
Current assessments of AI performance are largely anecdotal and heavily reliant on human oversight. Formal benchmarks are underutilised, leaving gaps in objective validation and scalability insights.
Embracing Latency-Relaxed Applications
A notable shift is toward latency-relaxed applications — those that aren’t hypersensitive to real-time delays.
This approach allows developers to focus on robust, non-urgent workflows, such as batch processing or analytical tools, rather than high-stakes, instantaneous responses.
Reliance on Off-the-Shelf Language Models
Standard commercial large language models (LLMs) dominate implementations, with little emphasis on fine-tuning or private hosting.
This plug-and-play strategy accelerates prototyping but raises questions about long-term customisation and data privacy.
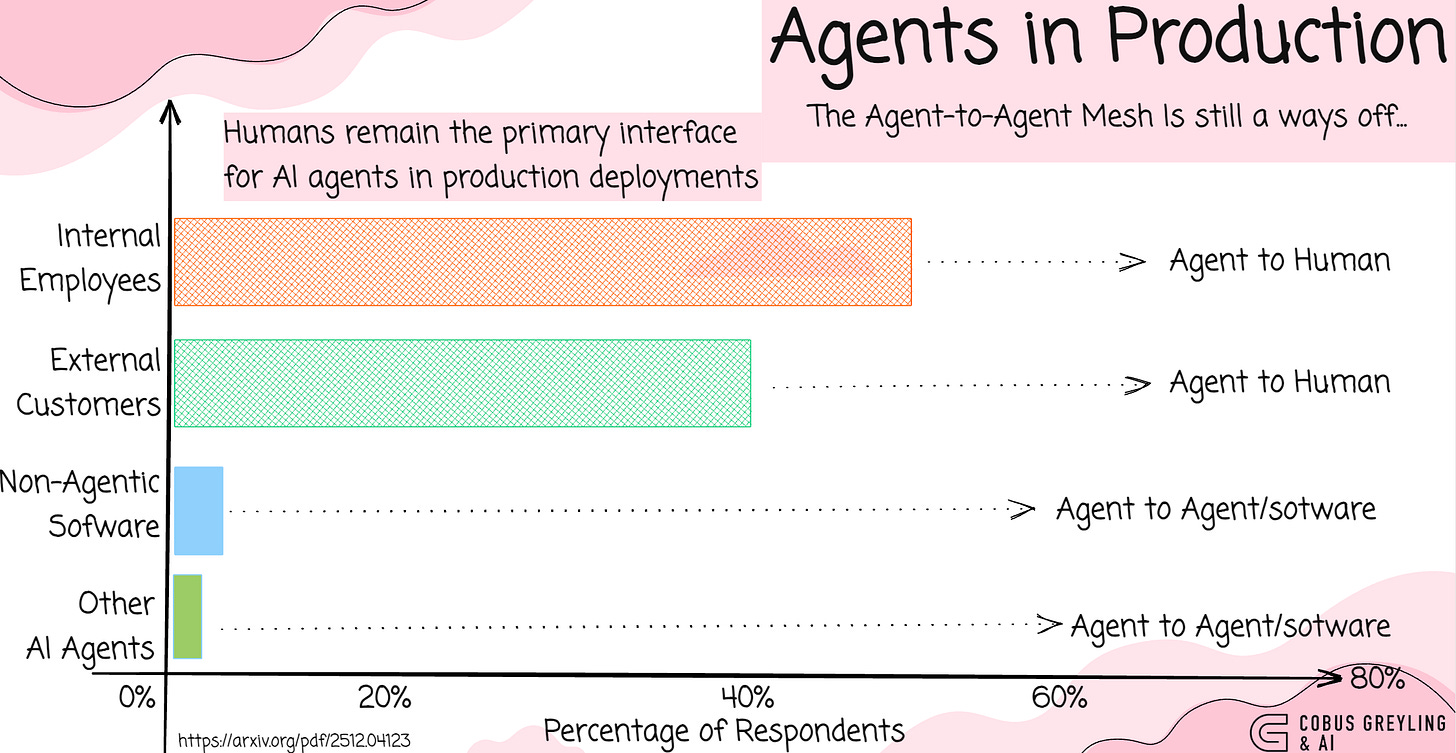
Internal Tools Over Customer-Facing Solutions
Internal-facing applications are the clear preference, outpacing customer-facing ones by a wide margin.
Machine-to-machine AI agents represent just 7% of deployments — tempering the hype around expansive AI agent meshes for the foreseeable future.
Building Custom Frameworks from Scratch
Rather than adopting third-party frameworks, developers are crafting their own tailored solutions.
This makes intuitive sense: It sidesteps the steep ramp-up period for learning external tools, mitigates irregularities or vendor-specific quirks, and provides greater control.
However, it also amplifies challenges like feature churn and rapid updates, which can strain maintenance efforts.
Human Oversight
Across agentic workflows, human intervention remains indispensable — not as a temporary crutch, but as a foundational safeguard.
This hybrid model ensures accountability, refines AI outputs in context.
More detail..
There has been a number of studies and research focussing real-world AI implementations.
A recent study surveyed 306 practitioners and conducting 20 in-depth case studies via interviews across 26 domains.
Production AI Agents are built using simple, controllable approaches with 68% execute at most 10 steps before requiring human intervention.
Deployment architectures favour predefined, structured workflows over open-ended autonomous planning to ensure reliability.
And 46.7% with less than 5 model calls before requiring human intervention. Tightly bounded autonomy.
70% rely on prompting off the-shelf models instead of weight tuning.
74% depend primarily on human evaluation, while 52% use LLM-as-a-judge.
Reliability remains the top development challenge, driven by difficulties in ensuring and evaluating AI Agent correctness.
This study looked at why organisations build AI Agents, how they build them, how they evaluate them, and what the top development challenges are…
A staggering 85% of detailed case studies do not use third-party agent frameworks, opting instead to build custom agent application from scratch.
Despite widespread excitement about agent potential, many question their real value and success in production whether agents can deliver on their promise and where their future lies.
75% evaluate their agents without formal benchmarks, relying instead on online-tests such as A/B testing or direct expert/user feedback.
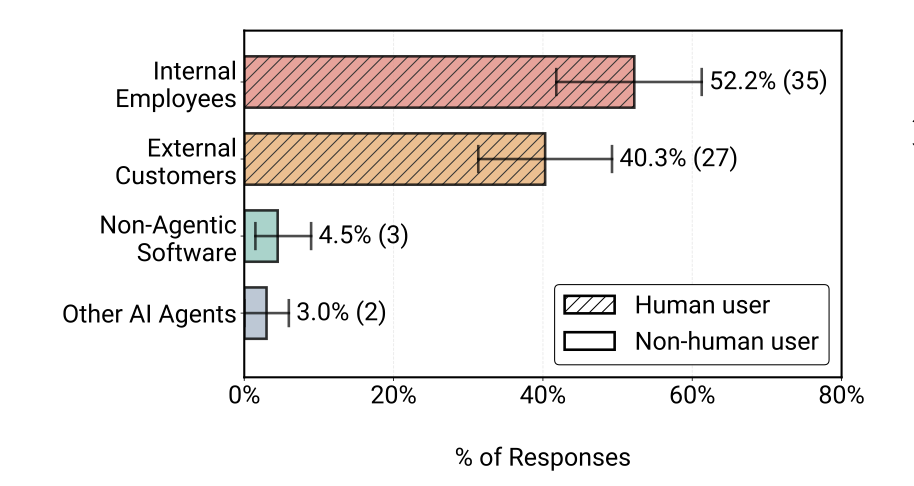
Internal employees are the primary user base (52.2%) for agents. Which makes sense, the level of cooperation you will get from employees as apposed to customers. This is followed by external customers(40.3%).
Only 7.5% of deployed systems serve non-human consumers.
Hence, deployed agents primarily serve human end-users (92.5%), which enables close human-oversight.
For obvious reasons developers focus on latency-relaxed applications.
Chief Evangelist @ Kore.ai | I’m passionate about exploring the intersection of AI and language. Language Models, AI Agents, Agentic Apps, Dev Frameworks & Data-Driven Tools shaping tomorrow.
Measuring Agents in Production
AI agents are actively running in production across diverse industries, yet little is publicly known about which…arxiv.org
COBUS GREYLING
Where AI Meets Language | Language Models, AI Agents, Agentic Applications, Development Frameworks & Data-Centric…www.cobusgreyling.com

Really appreciate this deep dive, Cobus. The clarity on how tightly bounded autonomy, human oversight, and custom frameworks drive real-world AI agent success is invaluable.
I talk about the latest AI trends and insights. If you’re interested in how AI agents are being deployed in real-world production and the strategies developers use to ensure reliability and human oversight, check out my Substack. I’m sure you’ll find it very relevant and relatable.
Excellent summary of the pragmatic reality behind agent deployments. The 85% custom framework stat is particulary telling - shows developers are optimizing for control over convenience, probably becuase off-the-shelf solutions don't map cleanly to their specific reliability constraints. The human-in-the-loop dominance (68% needing intervention within 10 steps) makes sense given current LLM limitations.